HPB-ALL
Cat.No.: CSC-C0497
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Blood; Peripheral Blood
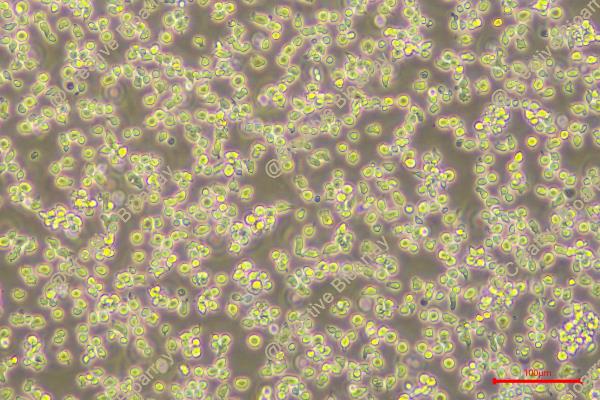
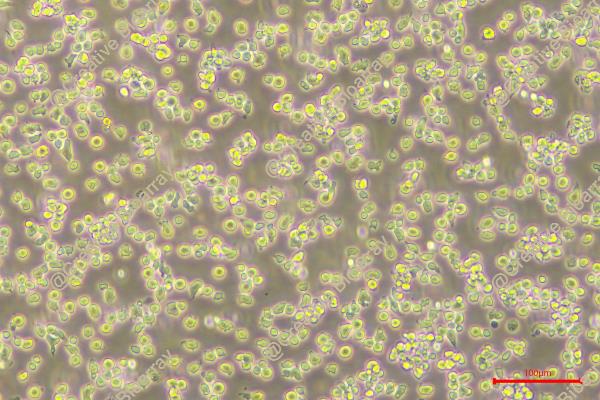
Morphology: round to polymorph cells growing singly or in clusters in suspension
Culture Properties: suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Documents
Immunology: CD2 +, CD3 +, CD4 +, CD5 +, CD6 +, CD7 +, CD8 +, CD13 -, CD19 -, CD34 -, TCRalpha/beta +, TCRgamma/delta -
Viruses: PCR: EBV -, HBV -, HCV -, HIV -, HTLV-I/II -, S
The HPB-ALL cell line was established in 1973 from the peripheral blood of a 14-year-old Japanese boy who was diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and thymoma at the time of diagnosis. The cells express markers associated with T-cell development, such as CD2, CD3, CD5, and CD7, but lack expression of more mature T-cell markers like CD4 and CD8. Cytogenetic analysis of the HPB-ALL cells has revealed a complex karyotype, with multiple chromosomal abnormalities typical of T-cell ALL.
The HPB-ALL cell line can be cultured in vitro and maintains its leukemic phenotype, making it a valuable model for investigating the biology and treatment of T-cell ALL. Researchers have utilized this cell line to study various aspects of T-cell transformation, signaling pathways, and drug sensitivity, contributing to the development of more effective treatments for patients with T-cell ALL.
Caspase-Independent Cell Death by FAS Ligation in HPB-ALL Cells
In HPB-ALL cells, a human thymus-derived T-cell line, Fas (CD95)-mediated cell death was inhibited by about only 50% as a result of treatment with an amount of benzyloxycarbonyl-Val-Ala-Asp-(O-methyl)-CH(2)F (zVAD-fmk) sufficient to block the caspase activity.
The cell death by the anti-human Fas antibody, CH11, was dependent on the concentration of CH-11 by the XTT method in HPB-ALL cells (Fig. 1A). Pretreatment with ZB4, which is known as Fas-neutralizing Abs, completely blocked cell death by CH-11 (Fig. 1B). By the treatment with 20 or 50 µM zVAD-fmk, this cell death was inhibited by about only 50% with CH-11 (Fig. 1A). The treatment of zVAD-fmk did not affect the cell viability in HPB-ALL cells (Fig. 1A). Under these conditions, the activation of caspase-3 by Fas ligation was inhibited completely by the treatment with 20 µM zVAD-fmk (Fig. 1C). By the treatment with 100 µM zIETD-fmk, which is a specific inhibitor of caspase 8, one of the initiator caspases, Fas-mediated cell death was also inhibited to the same extent as in the zVADfmk treatment in HPB-ALL cells (Fig. 1D). Next, the effect of the treatment of zVAD-fmk on Fas-mediated cell death were examined in other human lymphoblast cell lines. In all four cell lines, Fas-mediated cell death was inhibited by the treatment with 20 µM zVAD-fmk, which was different from the results for the HPB-ALL cells (Fig. 1E).
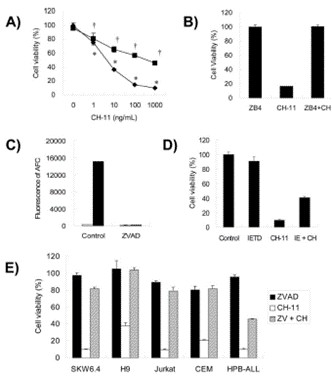 Fig. 1 Effect of zVAD-fmk on Fas-mediated cell death in HPB-ALLs. (Nakayama J, et al., 2007)
Fig. 1 Effect of zVAD-fmk on Fas-mediated cell death in HPB-ALLs. (Nakayama J, et al., 2007)
The Oxidation of EGCG Inhibits HPB-ALL Cell Lines via the Regulation of Notch1 Expression
T-cell ALL (T-ALL) is an aggressive hematological malignancy, and commonly associated with activating mutations in the Notch1 pathway. (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) has been shown to regulate Notch signaling. The chemical oxidation of EGCG has been reported under various oxidative conditions. EGCG was reacted with to yield the EGCG oxides 2-4 in 1.3-6.3% yields (Fig. 2).
To investigate the effects of compound 3 on the Notch1 signaling pathway, the expression of Notch1 and the downstream proteins in HPB-ALL cells were examined (Fig. 3). As shown in Fig. 3B-F, HPB-ALL cells were treated with compound 3 at the concentration of 5, 10, 20, 40, 60 μM for 12 h and the expression level of Notch1, cleaved-Notch1, c-Myc, and Hes1 were significantly decreased. Meanwhile, the expression of proliferation marker Ki67 was significantly reduced (Fig. 3B and G). These findings suggest that compound 3 inhibited the proliferation of HPB-ALL cells be through down-regulating the expression of Notch1 and Ki67. Compound 3 significantly induced Annexin V-positive apoptotic cells in HPB-ALL cells (Fig. 4A and B). Moreover, compound 3 induced the expression levels of caspase 3, caspase 9, and PARP 1, and increased the expression levels of cleaved-caspase 3, cleaved-caspase 9, and cleaved-PARP 1 (Fig. 4C-F).
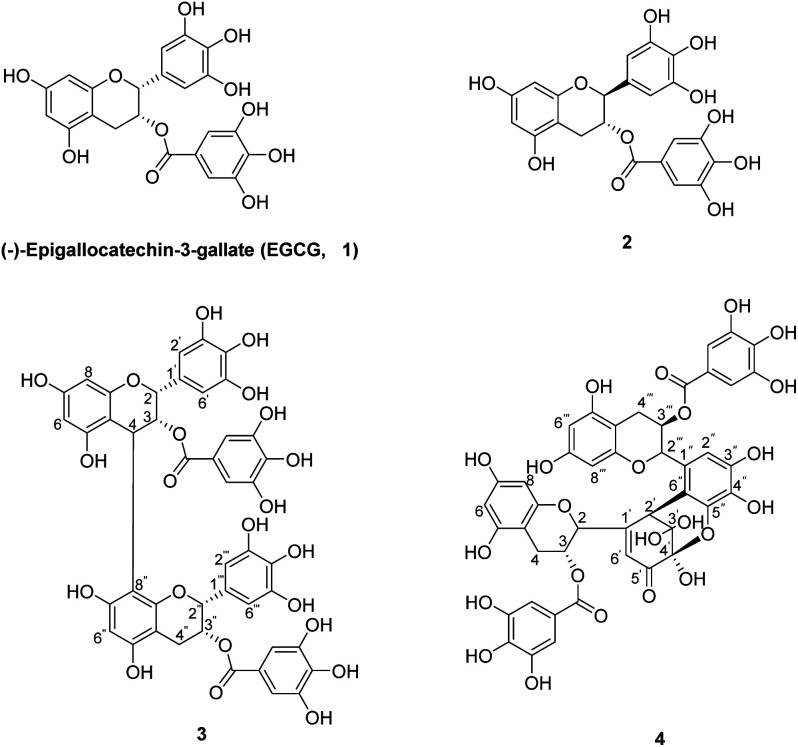 Fig. 2 The chemical structures of EGCG (1) and its oxides (2-4). (Wang YN, et al., 2020)
Fig. 2 The chemical structures of EGCG (1) and its oxides (2-4). (Wang YN, et al., 2020)
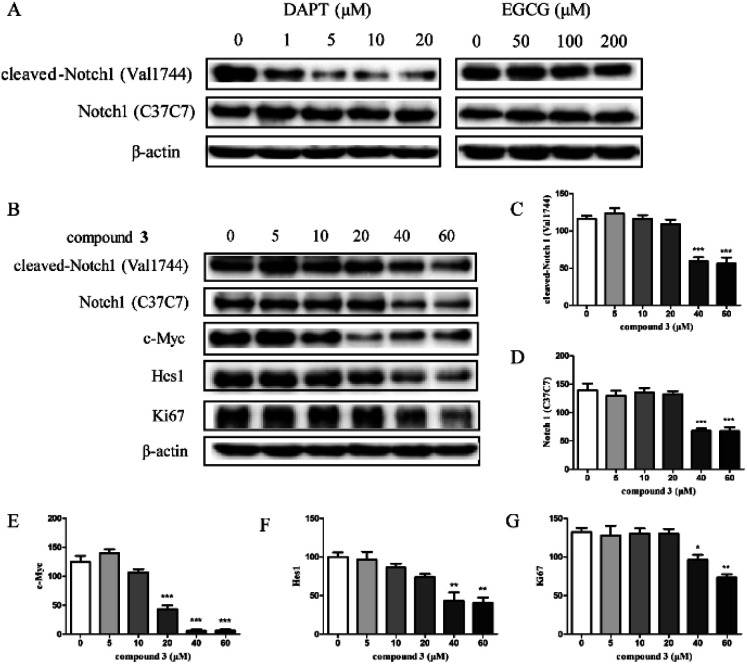 Fig. 3 The effect of compound 3 on Notch1 processing and downstream signaling pathway in HPB-ALL cells. (Wang YN, et al., 2020)
Fig. 3 The effect of compound 3 on Notch1 processing and downstream signaling pathway in HPB-ALL cells. (Wang YN, et al., 2020)
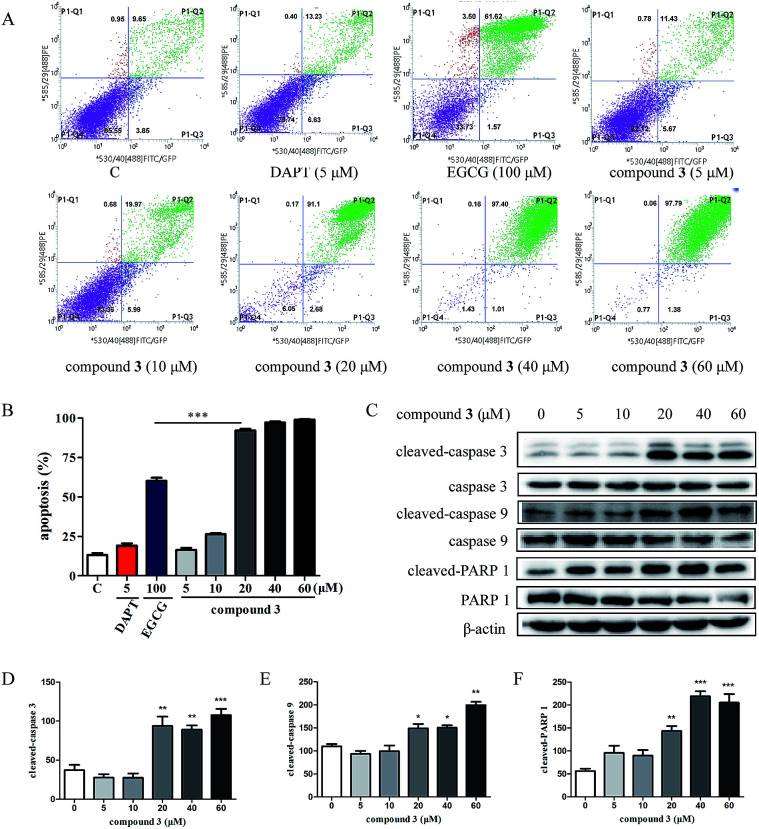 Fig. 4 Compound 3 induces apoptosis in HPB-ALL cells. (Wang YN, et al., 2020)
Fig. 4 Compound 3 induces apoptosis in HPB-ALL cells. (Wang YN, et al., 2020)
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells