NG108-15
Cat.No.: CSC-C9116W
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
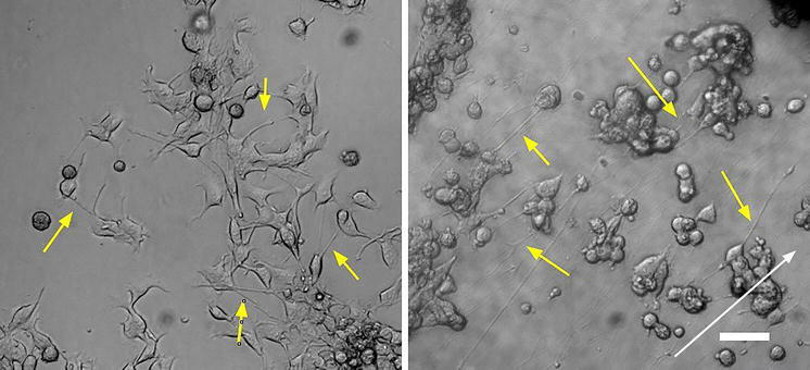
Morphology: flat; round; 10 to 100 micrometers diameter
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
NG108-15 is a hybrid cell line of neuroblastoma (neuronal precursor) and glioma (glial) origin created by somatic cell hybridization of the rat glioma cell line C6-BU-1 and mouse neuroblastoma cell line N18TG2. These cells are largely neuron-shaped, and display synapse-like structures upon conditions of differentiation. Because NG108-15 cells express high levels of δ- and κ-opioid receptors they play a crucial role in neuropharmacology research and GPCR signal transduction studies. NG108-15 cells show voltage-gated ion channel activity and the capability to differentiate into neuron-like cells which produce action potentials. As a result, because of its hybrid nature, the NG108-15 cell line has become a model used in various opioid drug mechanism, neurodegenerative disease, and synapse functionality research projects and is a commonly used neuroscientific tool. These cells are cultivated in a high-glucose DMEM medium with serum supplementation and can have their neuronal characteristics enhanced by induction of cAMP to complete differentiation.
The Effect of Rap on the Viability and Autophagy of NG108-15 Cells
The earlier studies showed that fluoride combined with aluminum (FA) can damage hippocampal neurons in the second-generation offspring (F2) of rats, but the mechanisms are still unknown. In this study, Tao’s team used F2 rat and NG108-15 cell models to explore the possible mechanisms.
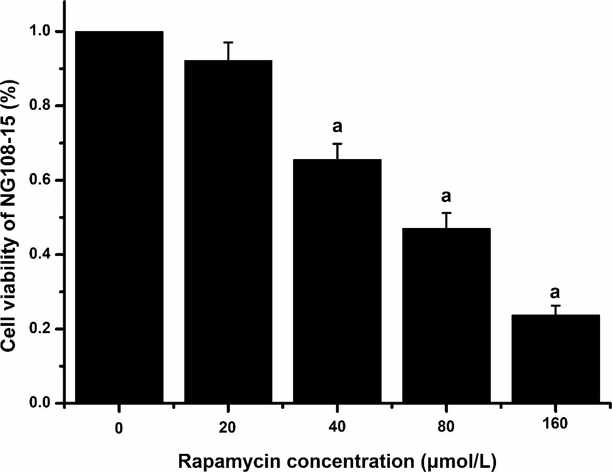
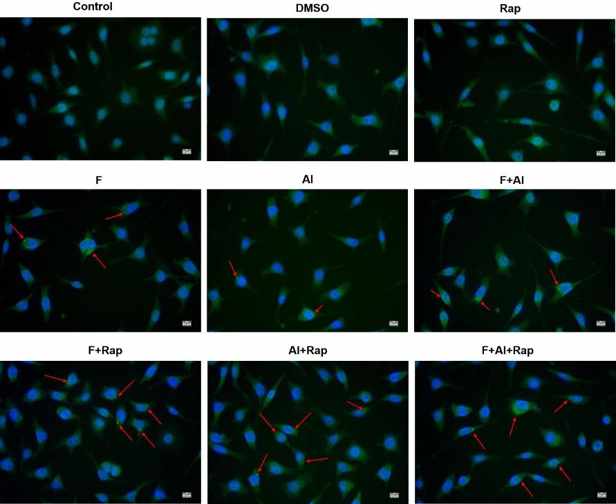
The viability of NG108-15 cells treated with 40, 80, 160 µmol/L Rap was lower than that of the control group (P < 0.05), shown in the Fig. 1. However, there was no significant difference in cell viability between the 20 µmol/L Rap group (92.16%) and the control group. The green fluorescent spots indicated the autophagy of NG108-15 cells. As shown in Fig. 2, no green fluorescent spots were observed in the cytoplasm of NG108-15 cells in the control, DMSO, and Rap groups. In contrast, green fluorescent spots were present in the cytoplasm of NG108-15 cells in the F, Al and F + Al groups. Compared to the DMSO group, the F + Rap, Al + Rap, and F + Al + Rap groups showed an increased intensity and volume of green fluorescent spots in the cytoplasm.
Xanthohumol Inhibits Cell Viability in NG108-15 Cells
Xanthohumol (XN), a flavonoid found in hops, has been reported to be an inhibitor of cancer cell growth. In the present study, Hu’s team investigated the effects of XN on NG108-15 cells with regard to cell viability, reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels and cell cycle progression, in order to evaluate the potential use of XN as an anti-neurotumor agent.
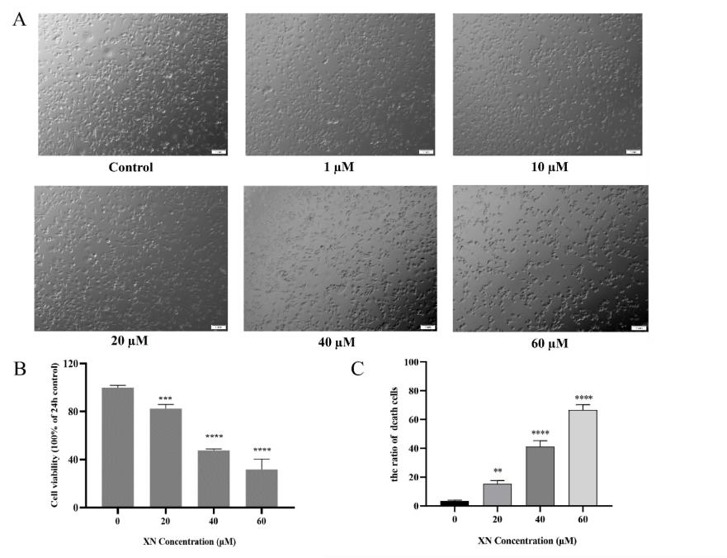
To evaluate the anti-glioma activity of XN, NG108-15 cells were treated with Xanthohumol (0–60 µM) for 24 h. High concentrations of XN (20–60 µM) inhibited the proliferation of NG108-15 cells, but low concentrations of XN (0–10 µM) had no effect on the viability of the cells as observed by phase-contrast microscopy (Fig. 3A). The cell viability and cell mortality were measured with CCK-8 and Trypan Blue assays, respectively, following 24 h of XN treatment (Fig. 3B and C). A dose-dependent inhibitory effect on NG108-15 cell proliferation by XN was observed. The calculated IC50 value was approximately 40 µM. The concentration of 40 µM XN was used in the following experiments.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells