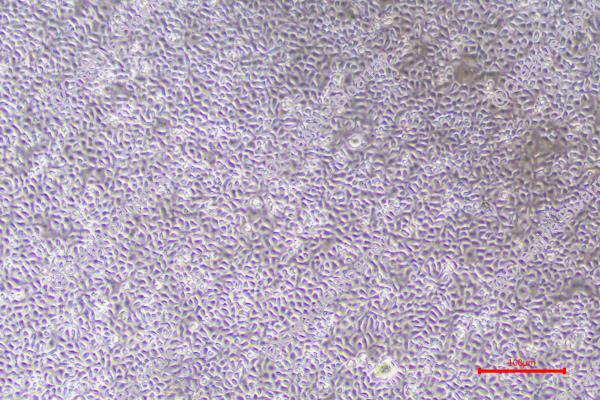
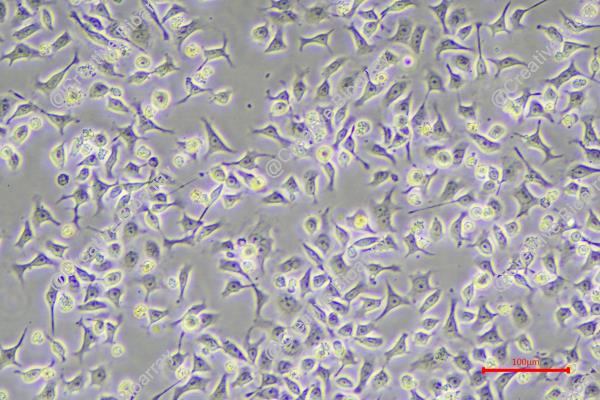
KYSE-180
Cat.No.: CSC-C0427
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Esophagus
Morphology: epitheloid cells growing as adherent monolayer
Culture Properties: monolayer
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 -, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 +, cytokeratin-18 +, cy
Derived from a primary esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) of a Japanese patient in the 1990s, the KYSE-180 cell line is a well-characterized, widely used in vitro model for ESCC research. It exhibits typical epithelial morphology, carries common ESCC genetic alterations (including mutations in TP53 and CDKN2A), expresses squamous differentiation markers such as cytokeratins, and demonstrates moderate invasive and migratory capabilities.
Current research applications heavily leverage KYSE-180 for drug discovery and therapeutic testing, especially for screening novel chemotherapeutics, targeted therapies (e.g., against EGFR, PI3K/mTOR pathways), and immunotherapies (e.g., checkpoint inhibitors such as anti-PD-1/PD-L1, often used in combination studies). It plays an important role in studying the molecular pathways driving ESCC progression, metastasis, and treatment resistance (e.g., EMT, apoptosis evasion), and serves as a backbone for genetic manipulation studies (knockdown/overexpression) to validate gene function. Its key strengths include: strong representation of ESCC biology (mutation profile, marker expression), robustness in standard cell culture conditions, consistent growth properties facilitating high-throughput assays, and extensive use in xenograft models for in vivo validation. This combination of relevance, reliability, and operability makes KYSE-180 an indispensable tool for advancing our understanding and treatment of this aggressive malignancy.
The Genomic Landscape of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Cell Lines
This study aims to elucidate the malignancy, invasion capability, classical cancer-related signaling pathways, and immune status of ESCC cell lines, providing a detailed genomic landscape and highlighting the unique features of each cell line.
Whole exome and RNA sequencing were conducted on ESCC cell lines TE-1, ECA-109, KYSE-30, KYSE-150, KYSE-180, KYSE-450, and KYSE-510, with the normal epithelium cell line Het-1a as a comparison. Bioinformatics methods analyzed gene mutation types, mutation frequencies, RNA expression, and classical cancer-related signaling pathways. Specific analyses were also performed on tumor burden, genes related to differentiation, invasion, immunity, and gene enrichment in each cell line.
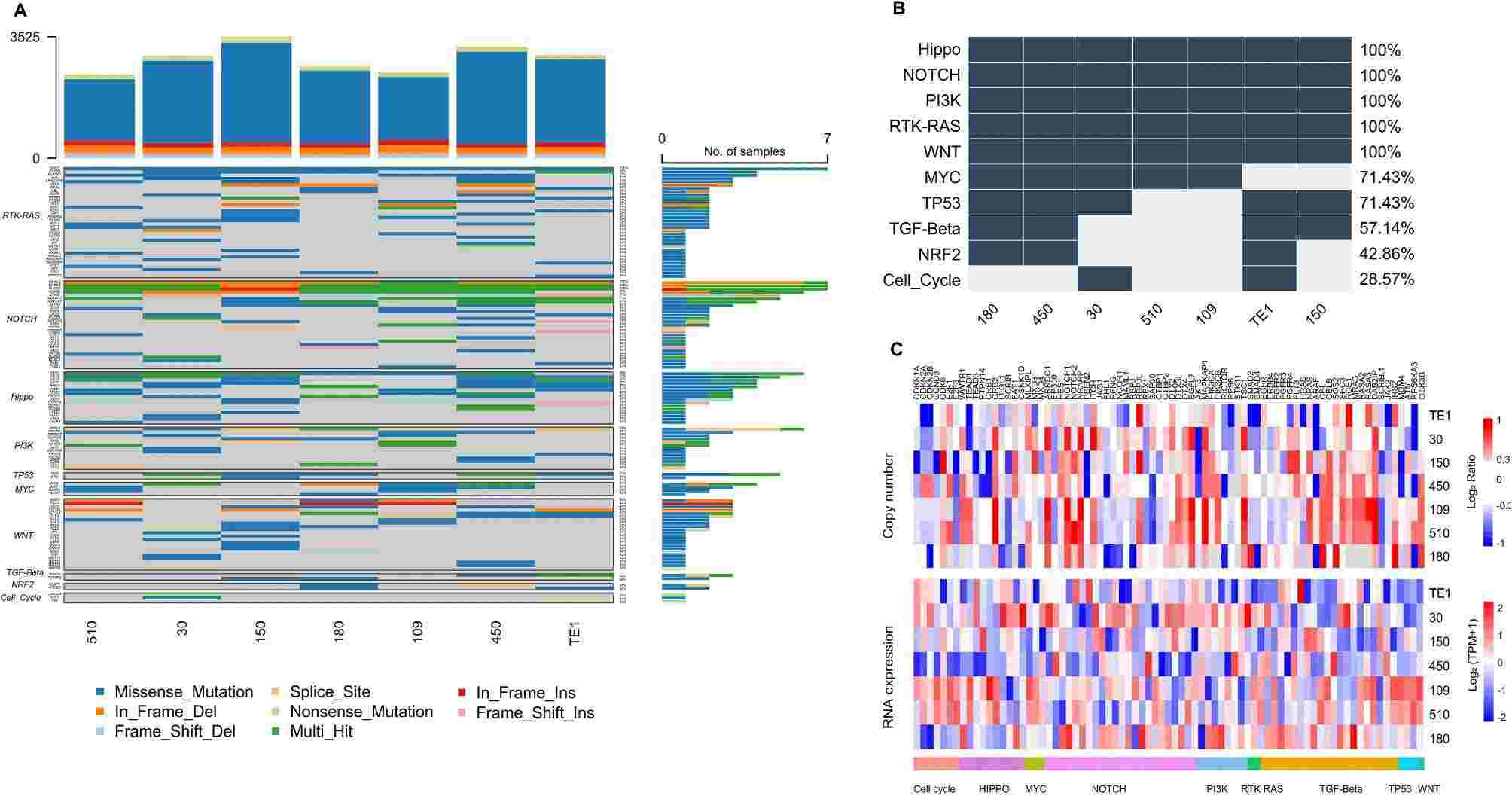 Fig. 1. Gene mutation in classical cancer-related signaling pathways (Zhang, Chao, et al. 2025).
Fig. 1. Gene mutation in classical cancer-related signaling pathways (Zhang, Chao, et al. 2025).
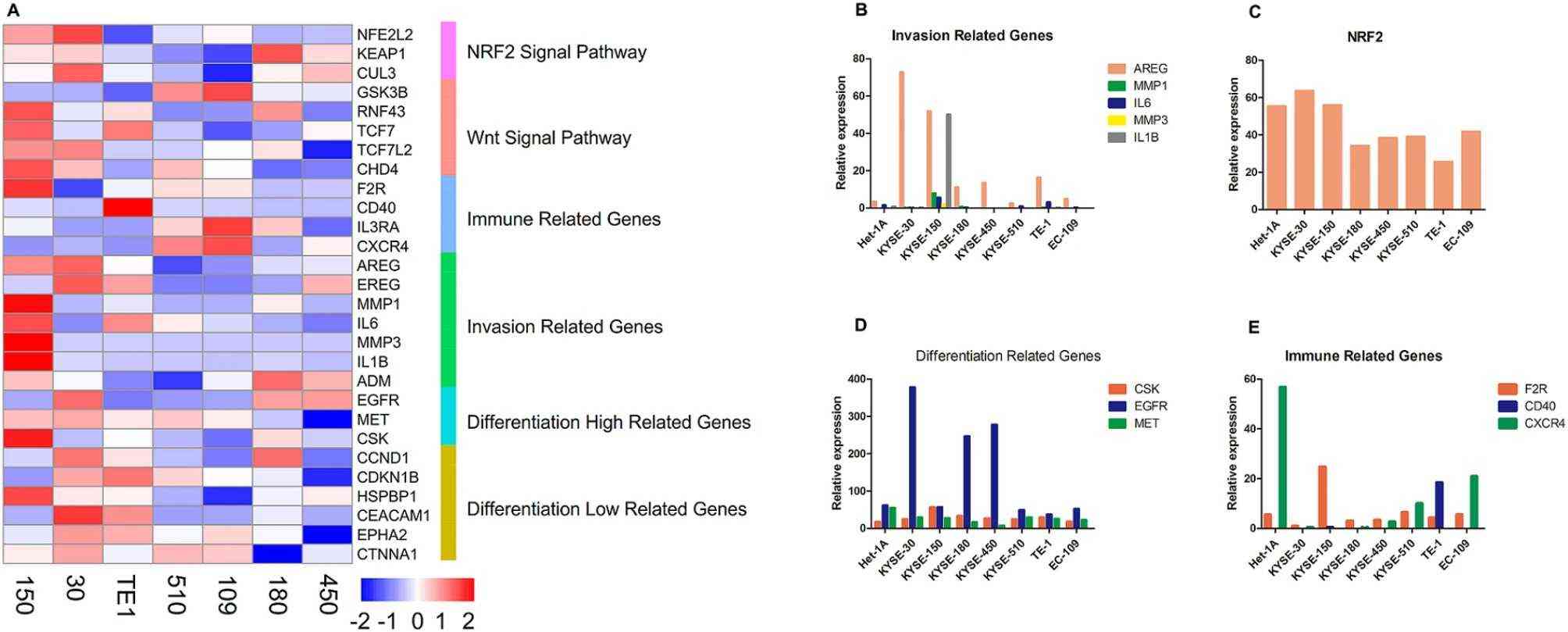 Fig. 2. The expression of oncogenic related genes (Zhang, Chao, et al. 2025).
Fig. 2. The expression of oncogenic related genes (Zhang, Chao, et al. 2025).
KLF13 Promotes Esophageal Cancer Progression
Kruppel-Like Factor 13 (KLF13) has strong effects on cancer occurrence and progression. Nevertheless, the role of KLF13 in esophageal cancer (EC) remain elusive. In this study, Pengjie Yang and his team detected the expression of KLF13 in EC tissues and cells using immunohistochemistry, western blot, and real-time PCR, and found that KLF13 was upregulated in EC tissues and cells compared to normal controls. High expression of KLF13 indicated a poor prognosis for EC patients. Further, function studies in vitro and in vivo were performed to explore the role of KLF13 in EC cell progression. The results revealed that KLF13 knockdown suppressed EC cell proliferation, migration, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, increased cell apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in vivo and inhibited tumor growth in vitro.
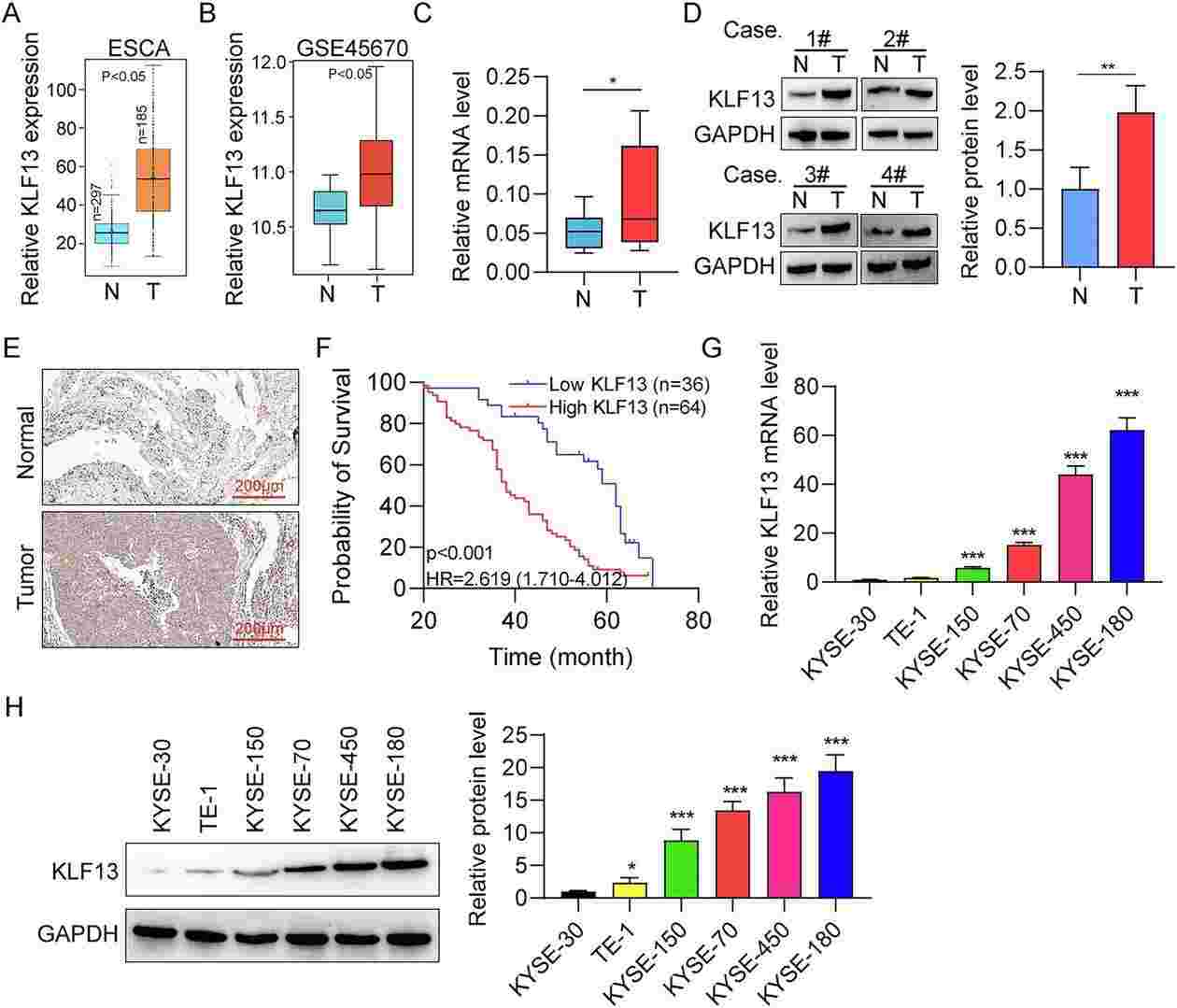 Fig. 3. KLF13 is highly expressed in EC (Yang, Pengjie, et al. 2025).
Fig. 3. KLF13 is highly expressed in EC (Yang, Pengjie, et al. 2025).
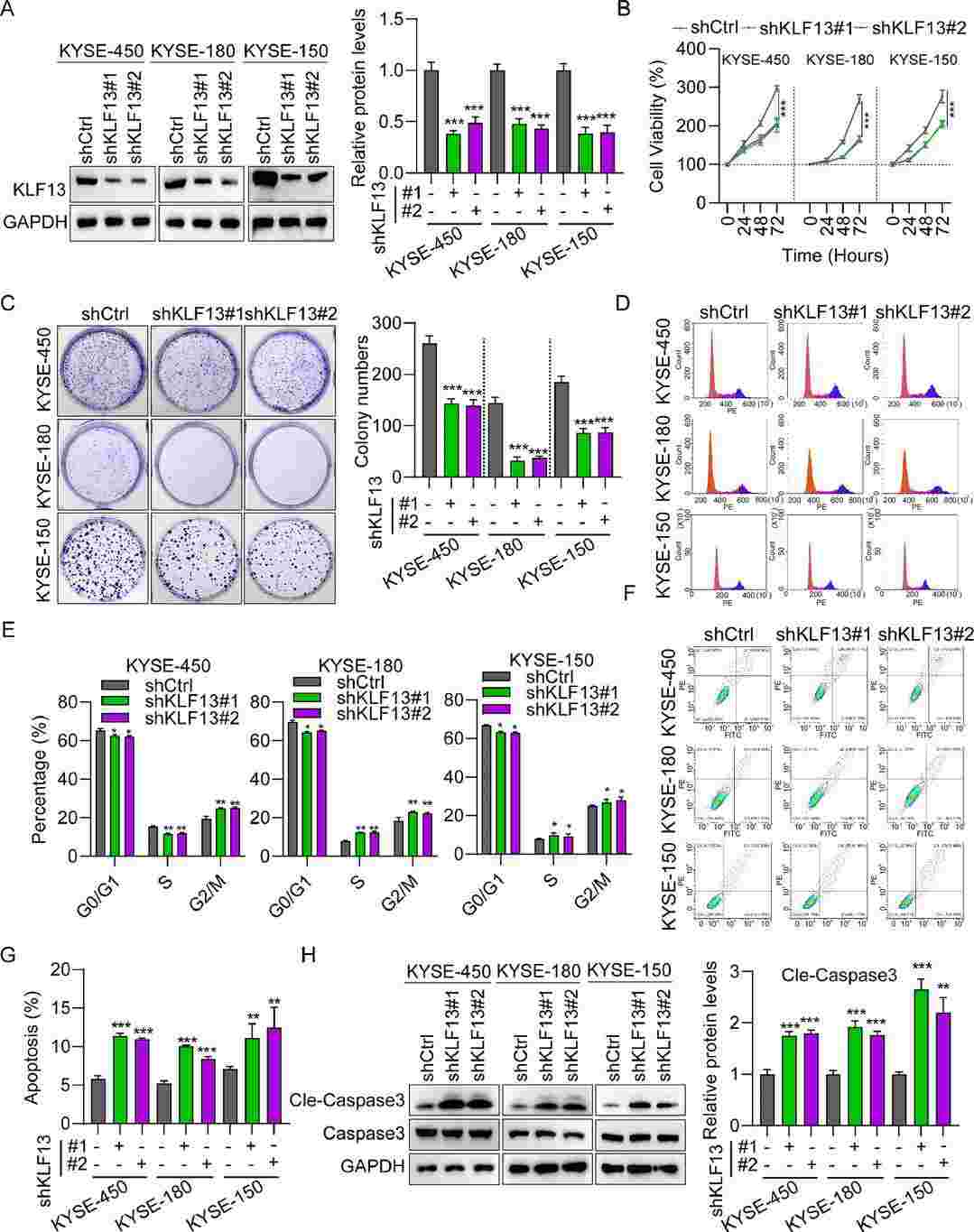 Fig. 4. Silencing KLF13 suppressed EC cell proliferation and migration (Yang, Pengjie, et al. 2025).
Fig. 4. Silencing KLF13 suppressed EC cell proliferation and migration (Yang, Pengjie, et al. 2025).
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells