HCT-15
Cat.No.: CSC-C0410
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Intestine; Colon
Morphology: epithelial
Culture Properties: Adherent
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
CSF1PO: 12
D13S317: 8,11
D16S539: 12,13
D5S818: 13
D7S820: 10,12
THO1: 7,9.3
TPOX: 8,11
vWA: 18,19
Immunology: cytokeratin +, cytokeratin-7 -, cytokeratin-8 +, cytokeratin-17 -, cytokeratin-18 +, cytokeratin-19 +, desmin -, endothel -, EpCAM +, GFAP -, neurofilament -
HCT‑15 is a human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line originally derived in the early 1970s from the primary colon tumor of a male patient with Dukes C disease. Morphologically, HCT‑15 cells grow in an epithelial‑like manner as an adherent monolayer with a cobblestone appearance. Clusters of floating cells are also found, which represents the cellular heterogeneity of solid tumors. On a cytogenetic level, HCT‑15 is hyperdiploid with multiple chromosomal aberrations. Most notably, it harbors the translocations t(8;17)(p23;q21) and inv(11)(p15.3;q13.1) as well as loss of chromosomes 8, 11 and 17. Molecularly, HCT‑15 has activating mutations in KRAS and loss‑of‑function alterations in TP53 that cause aggressive growth and intrinsic resistance to a variety of chemotherapeutic agents. It is carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-expressing (~5.4 ng per 10⁶ cells per 10 days), keratin-positive but CSAp-negative on immunocytochemical staining.
In vivo, the cell line readily forms tumors in nude mice with a 100 % take rate within three weeks and is thus a reliable xenograft model for sub‑cutaneous and orthotopic colon cancer studies. Its pronounced resistance to 5‑fluorouracil, SN‑38 (active metabolite of irinotecan) and taxanes has allowed for the creation of several drug‑resistant sub‑lines, e.g., HCT‑15/FU, that are widely used to study chemoresistance mechanisms.
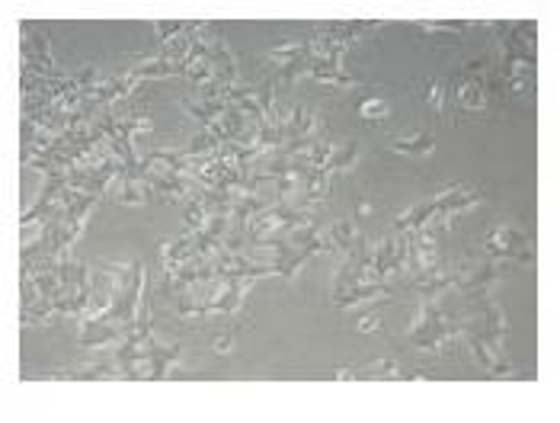

Biogenic PR-Agnps Inhibit Cell Proliferation in Colon Cancer HCT-15 Cells
Biosynthesized nanoparticles show promise in improving chemotherapy effectiveness, but there is limited research on biogenic silver nanoparticles from terrestrial ferns. Datkhile et al. investigated the effects of silver nanoparticles synthesized from Pteridium revolutum on inhibiting proliferation and inducing apoptosis in HCT-15 cancer cells.
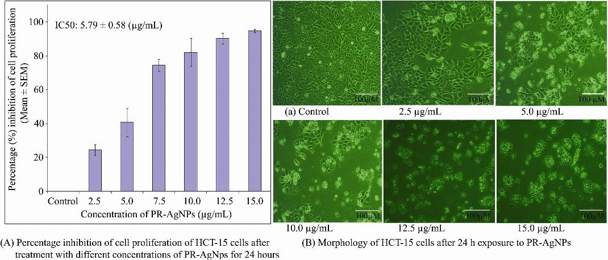
In vitro studies evaluated the inhibitory effects of biogenic PR-AgNPs on HCT-15 colon cancer cells. PR-AgNPs exhibited dose-dependent cytotoxicity (2.5-15.0 µg/mL), with cell viability decreasing as concentration increased (Fig. 1A). MTT assay results showed significant suppression of HCT-15 cell proliferation after 24 h, with IC50 and IC90 values of 5.79±0.58 µg/mL and 13.82±1.38 µg/mL, respectively. Complete growth inhibition was achieved at 15 µg/mL. Morphological changes, including cell shrinkage, were observed in HCT-15 cells treated with 10-15 µg/mL PR-AgNPs (Fig. 1B), contrasting with healthy control cells. PR-AgNPs induced intracellular suicide in HCT-15 cells, leading to compromised cell membrane integrity, cytoplasmic condensation, and apoptotic cell death. Normal fibroblast cells from breast cancer tissue exhibited low toxicity when exposed to PR-AgNPs. Even at 15 µg/mL, PR-AgNPs inhibited less than 40.70±11.83% of fibroblast cell growth after 24 h.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells