COLO 320 HSR
Cat.No.: CSC-C9363L
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
Source: Intestine; Colon
Morphology: rounded and refractile
Culture Properties: The cells grows loosely attached and in suspension
- Specification
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
CSF1PO: 11
D13S317: 11
D16S539: 11/12
D5S818: 12
D7S820: 9/12
THO1: 9
TPOX: 8/9
vWA: 15/18
D3S1358: 17
D21S11: 33.2
D18S51: 15
Penta E: 11
Penta D: 9/12
D8S1179: 13
FGA: 20 , 2010.
COLO 320 HSR is a human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line established from a primary colon tumor of a 43-year-old patient that was metastatic to the bone marrow, and has highly aggressive properties. The "HSR" in its name stands for cytogenetic markers for oncogene amplification (e.g. MYC) found on its chromosomes. The cells are round, highly refractive, loosely adherent as well as growth in suspension. These cells demonstrate both epithelial-like morphology and the ability to form tumors. A sister cell line of COLO 320 HSR, called COLO 320 DM, which is also from the same patient, is adherently growing, but has MYC gene amplification in the form of double-minute chromosomes (DM) rather than HSR.
In research, the COLO 320 HSR cell line has been used to study the aberrant expression and regulation of the c-MYC gene. MYC oncogene overexpression links to colon cancer progression while RNA interference (RNAi) targets the c-MYC gene to understand its impact on cell growth and programmed cell death. In addition, the cell line is commonly used for general anti-tumor drug screens, such as screening for the inhibitory effects of c-MYC antisense oligonucleotides or siRNA on cell proliferation. In cancer biology research, the COLO 320 HSR cell line is used as a model system to study the molecular mechanisms, signaling pathways, and potential therapeutics of colorectal cancer, such as MYC driven metabolic reprogramming and drug resistance.
ecDNA Hubs Drive Cooperative Intermolecular Oncogene Expression
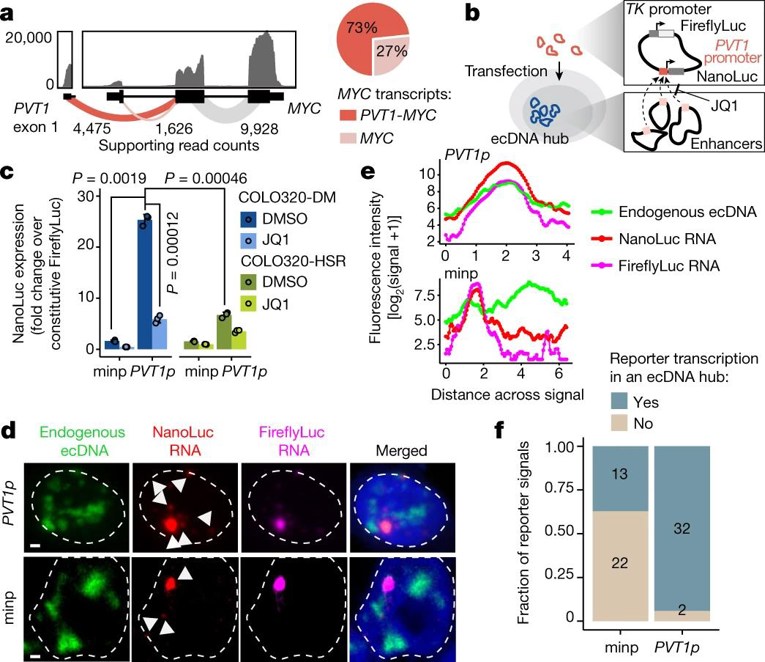
Extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA) is prevalent in human cancers, where it contributes to oncogene overexpression by amplification and deregulation. Although gene activation is commonly explained by cis-regulatory elements on the same chromosome, the functional relevance of ecDNA clustering is not well understood. Here, Hung et al. explored how ecDNA hubs—clusters of 10–100 ecDNAs located in discrete nuclear bodies—facilitate intermolecular enhancer-gene communication and oncogene overexpression, and their potential as therapeutic vulnerabilities.
To test if ecDNA spatial clustering enhances transcription, they designed a plasmid with a PVT1 promoter-driven NanoLuc reporter (PVT1p-nLuc) and a TK promoter-driven Firefly luciferase control (Fig. 1b). In ecDNA+ COLO320-DM cells, the activity of PVT1p was 25-fold higher than that from minimal promoters and 4-fold higher than in ecDNA− COLO320-HSR cells (Fig. 1c). Suppression of PVT1p activity by low dose JQ1 (which breaks up ecDNA hubs) was strong in COLO320-DM (5-fold) but mild in COLO320-HSR (2-fold) (Fig. 1c). DNA/RNA FISH analysis revealed that PVT1p-driven NanoLuc transcription was enhanced in the vicinity of ecDNA hubs (Fig. 1d–f). The addition of a cis-enhancer significantly increased both reporters but ablated the differential JQ1 sensitivity between the two cell lines. These data confirm trans-activation of PVT1p by ecDNA hubs.
Tir-induced Cell Death is Dependent on Caspase-4 and GSDMD
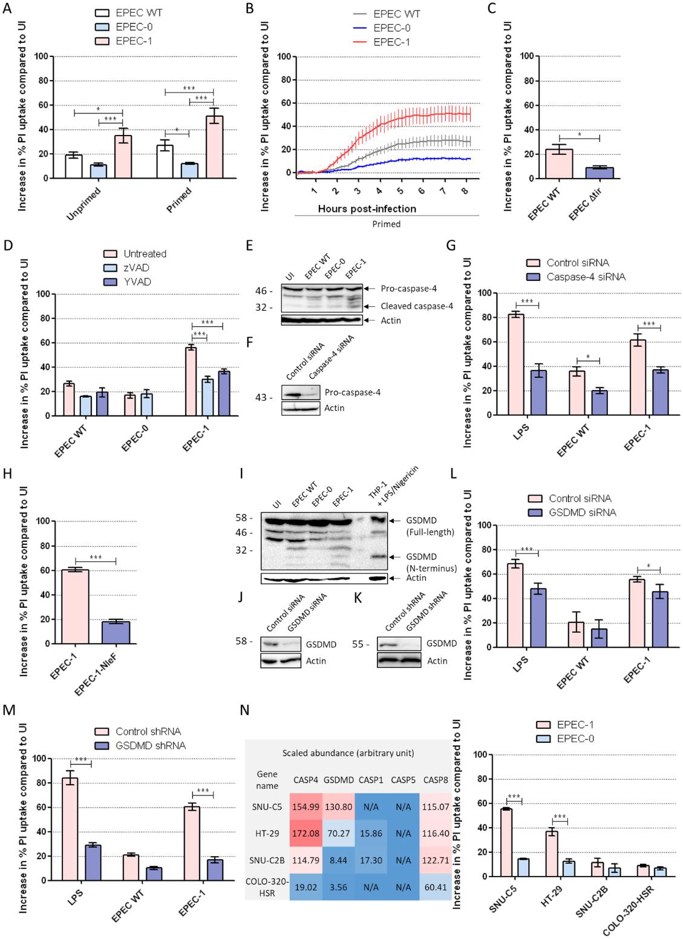
Enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) is a diarrhoeagenic pathogen that colonizes intestinal cells through its type III secretion system (T3SS). One of EPEC’s effectors Tir has been shown to induce actin polymerisation and pyroptosis in macrophages but its activity in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) is unknown. To address this, Zhong’s team utilized IECs infected with EPEC to test various parameters to confirm Tir-dependent pyroptosis including calcium chelation, caspase-4/GSDMD knockdown, and translocation of NleF, a caspase-4 inhibitor.
Results showed that caspase inhibitors (zVAD/YVAD) reduced EPEC-1-induced IEC death, confirming pyroptosis, while apoptosis (PARP1 cleavage) and necroptosis (Nec1/NSA) were ruled out (Fig 2D, S2). Caspase-4 silencing or NleF expression blocked cell death, and GSDMD cleavage was detected (Fig 2E–I). GSDMD knockdown significantly suppressed pyroptosis (Fig 2K–M), though residual death (~15%) remained unexplained. To confirm a causal relationship between GSDMD and cell death, three other IEC lines with relatively lower abundance of GSDMD (1.9–36.7×, less than SNU-C5, Fig 2N, left) but similar levels of caspase-4 were assessed (HT-29, SNU-C2B, COLO-320-HSR). All three had undetectable levels of caspase-5. Moreover, all IEC lines had intact EPEC adhesion and Tir translocation into cells. IFNγ-primed SNU-C5 and HT-29 had elevated EPEC-1-induced death relative to EPEC-0, while COLO-320-HSR and SNU-C2B with low levels of GSDMD were resistant to Tir-dependent death (Fig 2N, right). The abundance of GSDMD directly correlated with Tir-induced pyroptosis.
Ask a Question
Write your own review
- You May Also Need
- Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells
- Human Neurons
- Mouse Probe
- Whole Chromosome Painting Probes
- Hepatic Cells
- Renal Cells
- In Vitro ADME Kits
- Tissue Microarray
- Tissue Blocks
- Tissue Sections
- FFPE Cell Pellet
- Probe
- Centromere Probes
- Telomere Probes
- Satellite Enumeration Probes
- Subtelomere Specific Probes
- Bacterial Probes
- ISH/FISH Probes
- Exosome Isolation Kit
- Human Adult Stem Cells
- Mouse Stem Cells
- iPSCs
- Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells
- iPSC Differentiation Kits
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Immortalized Human Cells
- Immortalized Murine Cells
- Cell Immortalization Kit
- Adipose Cells
- Cardiac Cells
- Dermal Cells
- Epidermal Cells
- Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- Umbilical Cord Cells
- Monkey Primary Cells
- Mouse Primary Cells
- Breast Tumor Cells
- Colorectal Tumor Cells
- Esophageal Tumor Cells
- Lung Tumor Cells
- Leukemia/Lymphoma/Myeloma Cells
- Ovarian Tumor Cells
- Pancreatic Tumor Cells
- Mouse Tumor Cells