Transporter Screening Service
- Overview
- Service Details
- Features
- FAQ
- Explore Other Options
The Solute Carrier (SLC) family is the second largest group of membrane transporters, comprising over 450 members across 65 gene families. These transporters mediate the uptake and exchange of amino acids, nucleotides, carbohydrates, vitamins, ions, metabolites, and drugs, and are essential for cellular homeostasis, metabolism, and signaling.
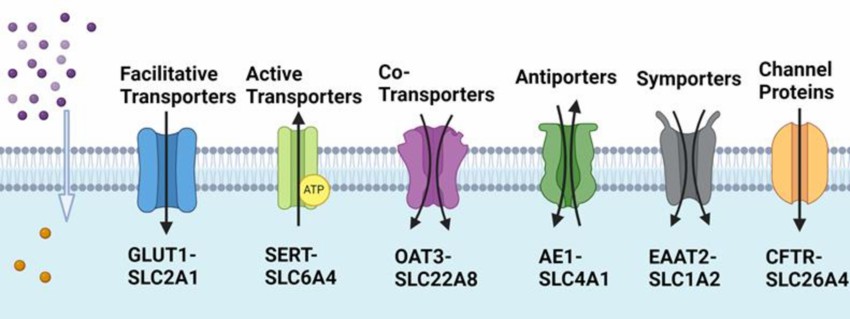 Fig. 1. Major SLC-transporters expressed in the plasma membrane facilitate the movement of substrates across cell membranes (Guntupalli V, Wan R J, et al., 2024).
Fig. 1. Major SLC-transporters expressed in the plasma membrane facilitate the movement of substrates across cell membranes (Guntupalli V, Wan R J, et al., 2024).
The ATP-Binding Cassette (ABC) family is a superfamily of membrane transporters that utilize the energy from ATP hydrolysis to actively efflux a diverse range of substrates including drugs, metabolites, lipids, and xenobiotics. ABC transporters are central to drug ADME processes and are key mediators of multidrug resistance (MDR), posing significant challenges in oncology and infectious disease treatment.
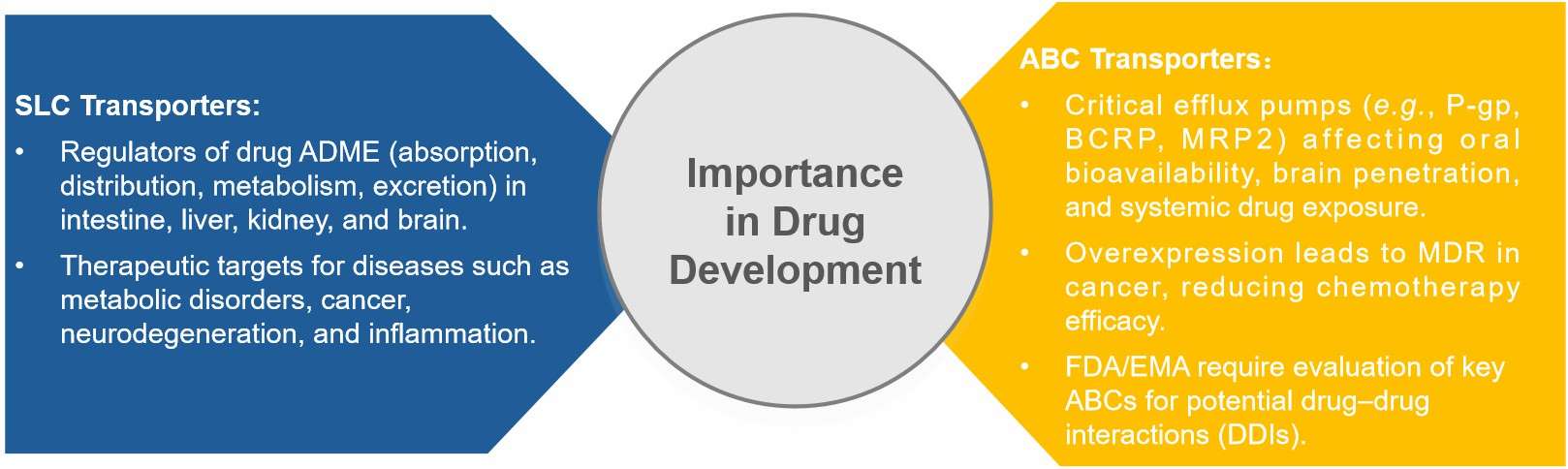
Our Transporter Screening Service
At Creative Bioarray, we provide comprehensive SLC and ABC transporter screening services, enabling data-driven decisions in drug discovery, safety assessment, and clinical development.
SLC Transporter
| Transporter Class | Subtypes |
| Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptides (OATP) | OATP1B1 (SLCO1B1) OATP1B3 (SLCO1B3) OATP2B1 (SLCO2B1) |
| Organic Anion Transporters (OAT) | OAT1 (SLC22A6) OAT3 (SLC22A8) |
| Organic Cation Transporters (OCT/OCTN) | OCT1 (SLC22A1) OCT2 (SLC22A2) OCTN1 (SLC22A4) OCTN2 (SLC22A5) |
| Multidrug And Toxin Extrusion Proteins (MATE) | MATE1 (SLC47A1) MATE2-K (SLC47A2) |
| Glucose Transporters (GLUT) | GLUT1 (SLC2A1) GLUT4 (SLC2A4) |
| Monocarboxylate Transporters (MCT) | MCT1 (SLC16A1) MCT4 (SLC16A3) |
| Amino Acid Transporters | LAT1 (SLC7A5) ASCT2 (SLC1A5) EAAT1 (SLC1A3) EAAT2 (SLC1A2) EAAT3 (SLC1A1) PEPT1 (SLC15A1) PEPT2 (SLC15A2) |
*Additional SLC transporters available upon request.
ABC Transporter
| Transporter Class | Subtypes |
| P-glycoprotein (P-gp / MDR1) | ABCB1 |
| Breast Cancer Resistance Protein (BCRP) | ABCG2 |
| Multidrug Resistance-Associated Proteins (MRP) | MRP2 (ABCC2) MRP3 (ABCC3) MRP4 (ABCC4) |
| Bile Salt Export Pump (BSEP) | ABCB11 |
| Other ABCs (available on request) | ABCC1 ABCC5 |
Custom ABC transporter panels can be tailored for oncology, CNS, or metabolic drug studies.
Advanced assay platforms
- Fluorescence-Based Screening Assays: High-throughput solutions for discovery of transporter modulators.
- Radiolabeled Substrate Uptake and Efflux Assays: Sensitive methods for quantifying transport activity of both SLC and ABC transporters.
- Membrane Vesicle Transport Assays (ABC-specific): Gold standard approach for evaluating ATP-dependent uptake/efflux activity.
- Electrophysiology Studies: Accurate characterization of transporter function using advanced SSM-based technology.
- Mass Spectrometry-Based Assays: Direct detection of drug and metabolite transport, offering high sensitivity and specificity
Key Features
Wide Coverage
Broad coverage of key SLC and ABC transporters recommended by FDA/EMA guidelines.
Multi-technology Platforms
Including fluorescence probes, membrane potential measurement, radioisotope assays, mass spectrometry, electrophysiology, etc.
High-throughput
Support for high-throughput screening (96/384-well plates) for rapid data collection.
Flexible Cell Models
Options include stably or transiently transfected cells, primary cells, or membrane vesicle systems.

Customizable Workflows
Fully customizable workflows, from target validation to drug interaction assessment.
FAQ
What is the difference between SLC transporters and ABC transporters?
SLC transporters mainly utilize concentration gradient or co-transport to achieve transmembrane transport of substrate molecules, while ABC transporters use the energy of ATP hydrolysis to actively transport substrates. They differ in the types of substrates they transport, energy requirements, and their roles in drug disposition and disease.
How are SLC transporters relevant to drug development?
SLC transporters play a significant role in drug ADME (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion). Understanding the interaction between drugs and SLC transporters can help optimize drug pharmacokinetic properties, improve efficacy, and reduce toxicity. Additionally, some SLC transporters are drug targets themselves.
Can multiple transporter activities be assessed simultaneously?
Yes, we support multi-target parallel assessments, significantly increasing efficiency, especially in early drug screening.
Do you provide screening services for substrates/inhibitors?
Yes, we offer services for identifying substrate identity, affinity measurements, and evaluating inhibition/activation effects for candidate molecules.
Do you offer screening for other SLC transporters not mentioned?
Certainly! We can customize screening panels according to your research needs, including specific transporters. Please contact our customer service for detailed requirements.
What types of detection technologies do you use in your assays?
We use a variety of cutting-edge detection technologies, including fluorescence-based detection, radiolabeled substrate assays, and electrophysiology measurements, tailored to the specific needs of your project.
Explore Other Options