A Report of Regase-2 Inhibiting Glioblastoma Cell Proliferation
Scientific Reports. 2024 Jan 18; 14 (1): 1574.
Authors: Sowinska W, Wawro M, Kochan J, Solecka A, Polak J, Kwinta B, Kasza A.
INTRODUCTION
Regnase-2 (Reg-2/MCPIP2/ZC3H12B) is uniquely expressed at a high level in the healthy brain and down-regulated in samples from patients with glioma, reaching the lowest level in high-grade glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). This RNase is involved in the regulation of neuroinflammation through the degradation of IL-6 and IL-1 mRNAs, key pro-inflammatory cytokines for GBM pathology. Reg-2 is a strong inhibitor of the proliferation of human glioblastoma cell lines and blocks their potential to form colonies.
METHODS
- Using the Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposon system we generated U87-MG cell lines with introduced sequences encoding WT Reg-2 (U87-Reg-2) or its mutein Reg-2-D/A (U87-Reg-2D/A) or luciferase (U87-luc) under the control of doxycycline (dox)-inducible promoter. Cells were stained with Far Red reagent and cultured for 48 h with/without dox. Cell division was tracked by measuring the fluorescent signal generated after the conversion of cell-permeable fluorescent molecules to their derivatives by intracellular esterases.
- To reveal the mechanisms responsible for Reg-2-dependent inhibition of proliferation, we analyzed its influence on the cell cycle. U87-Reg-2, U87-Reg-2D/A and control cells were stained with propidium iodide dye, and the number of cells in the individual phases of the cell cycle was estimated by flow cytometry.
- To identify mRNA targets implicated in cell cycle regulation, we have performed an RNAseq analysis of the transcriptome of U251-MG human glioblastoma cells overexpressing Reg-2 or luciferase (control). Obtained results have been deposited in NCBI's Gene Expression Omnibus and are accessible through GEO Series accession number GSE248634. To study the mechanisms of observed changes in transcript levels we have employed RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP).
- Browse our recommendations
| Product/Service Types | Description |
| Cell Proliferation Assay Services | Creative Bioarray provides cell proliferation assay services for our customers. We are capable of performing different cell proliferation assays based on several concepts, which are measuring the rate of DNA replication, analysis of metabolic activity, cell surface antigen recognitions, detecting proliferation markers, ATP measurement, measures of membrane integrity, and so on. |
| Cell Cycle Assays | Creative Bioarray provides cell cycle analysis services for all of our customers, we use flow cytometry to measure cellular DNA content. Different dyes can be chosen to perform the assays, including propidium iodide (PI), BrdU, 7-amino actinomycin-D (7-AAD), Hoechst 33342 and 33258, and 4'6'-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI), based on the customer's applications or requirements. |
| Cell Cytotoxicity Assay Kit | Cell proliferation assays are used to monitor the dynamic growth of a cell population or to detect daughter cells in a growing population. |
| Cell Cycle Analysis Kit | Creative Bioarray's cell cycle analysis kit provides a quick and easy method to detect the number of cells in a cell population, which are at a specific stage of the cell cycle. |
RESULTS
- The influence of Reg-2 on another human glioblastoma cell line derived from a malignant glioblastoma tumor, U87-MG, was analyzed. The time-dependent increase in the cell number is blocked when WT Reg-2 is expressed. The number of U87-Reg-2 cells remains almost constant within 72 h of their culture in a medium containing dox. Simultaneously, the proliferation of control U87-luc cells under the same conditions remains exponential within the examined period with a doubling time of approx. 24 h.
- The shift toward higher intensity of the peak in U87-Reg-2 cells treated with dox. Such an outcome suggests that induction of Reg-2 overexpression results in slower proliferation of U87-Reg-2 cells. The effect of ribonucleolytic inactive mutein (Reg-2-D/A) on U87 cell proliferation is much weaker. To further determine the influence of Reg-2 on cell division we performed a clonogenic assay. Reg-2 overexpression strongly inhibits glioma cell division and its potential to form colonies. This regulation requires an intact NYN/PIN domain as the effect of nucleolytic-inactive Reg-2-D/A on colony formation was similar to in the control cells.
- After dox induction, the population in phase G1 increases from ~ 70% in control to ~ 80% in U87-Reg-2 cells. A similar but much weaker trend is observed in U87-Reg-2D/A cells. The S phase is not significantly affected by Reg-2 overexpression in investigated cells. Cells in the G2 phase accounted for ~ 11% of U87-Reg-2, ~ 13% of U87-Reg-2D/A, and ~ 16% in control cells. We concluded that Reg-2 stalls U87-MG glioblastoma cells in the G1 phase.
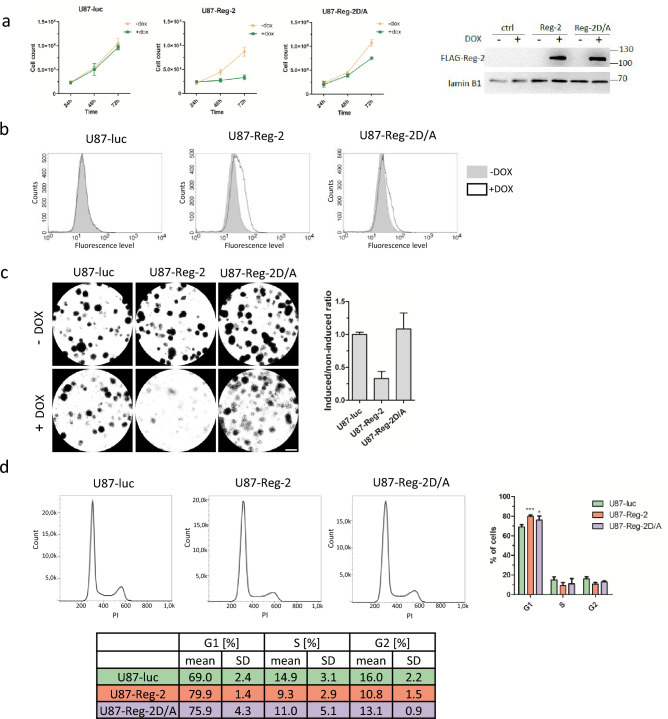 Fig. 1 Regnase-2 inhibits proliferation, and stalls the cell cycle at the G1 phase.
Fig. 1 Regnase-2 inhibits proliferation, and stalls the cell cycle at the G1 phase.
- Of the 29 analyzed transcripts encoding proteins involved in the regulation of proliferation, 21 mRNAs encoding cyclins, kinases, and regulatory proteins were significantly down-regulated by Reg-2. The levels of CCND1, CCNE2, and CCNA2 are down-regulated by Reg-2 independently of the active nucleolytic domain. PCR analysis of immunoprecipitated mRNAs reveals direct binding of Reg-2 to all tested transcripts. As a positive control, we have used IL-6 mRNA and, as a negative control, POLE4 mRNA. Reg-2 is bound to the IL-6 transcript and does not interact with POLE4 mRNA.
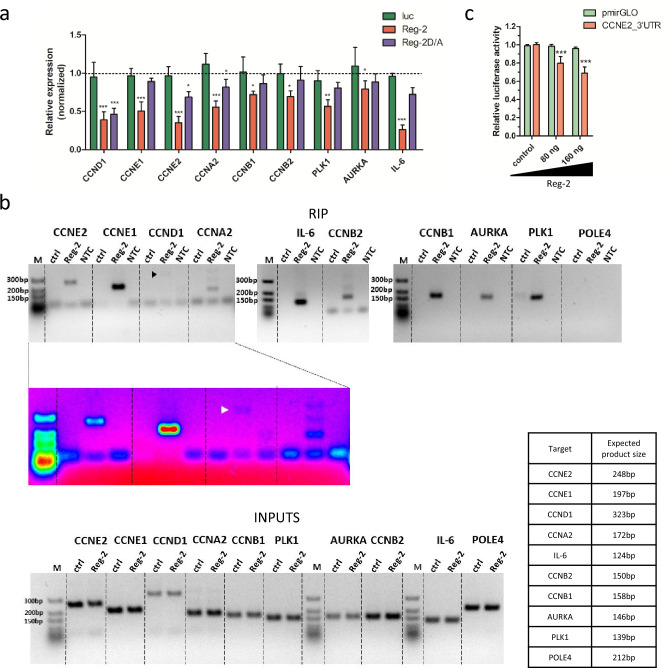 Fig. 2 Reg-2 regulates the level of transcripts down-regulated in glioblastoma samples and is involved in cell cycle regulation.
Fig. 2 Reg-2 regulates the level of transcripts down-regulated in glioblastoma samples and is involved in cell cycle regulation.
SUMMARY
Overexpression of Reg-2 stalls glioblastoma cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle and reduces the level of transcripts implicated in cell cycle progression. These newly identified targets include CCND1, CCNE1, CCNE2, CCNA2, CCNB1, and CCNB2, encoding the cyclins as well as AURKA and PLK1, encoding two important mitosis regulators. By RNA immunoprecipitation we confirmed the direct interaction of Reg-2 with the investigated transcripts. In conclusion, our results indicate that Reg-2 controls key elements in GBM biology by restricting neuroinflammation and inhibiting cancer cell proliferation.
RELATED PRODUCTS & SERVICES
Reference
- Sowinska W, et al. (2024). "Regnase-2 inhibits glioblastoma cell proliferation." Sci Rep. 14 (1): 1574.