Featured Products
Our Promise to You
Guaranteed product quality, expert customer support

NALM-6
- Specification
- Technical Resources
- Recommended Products
- Background
- Scientific Data
- Q & A
- Customer Review
- Product Information Sheet
The NALM-6 cell line was derived from the peripheral blood of a 19-year-old male patient who had experienced a relapse of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). ALL is a type of cancer that primarily affects lymphoid progenitor cells and is characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of immature lymphocytes. NALM-6 cells exhibit several characteristic features of B-cell precursor ALL. They express surface markers typically seen in B-cell lineages, such as CD19, CD10, and CD24.
Researchers have utilized the NALM-6 cell line to study the molecular mechanisms underlying leukemogenesis, signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation and survival, genetic alterations associated with ALL, and the development and evaluation of targeted therapies. The NALM-6 cell line has been instrumental in advancing our understanding of the biology of ALL and has contributed to the development of new treatment strategies. Moreover, the NALM-6 cell line has been used as a model system for drug screening and testing the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents and targeted therapies against ALL.
Investigation of Decitabine Effects on NALM-6 Cell Lines
Decitabine is a potent anticancer hypomethylating agent and changes the gene expression through the gene's promoter demethylation and also independently from DNA demethylation. So, the present study was designed to distinguish whether Decitabine, in addition to inhibitory effects on DNA methyltransferase, can change HDAC3 and HDAC7 mRNA expression in NALM-6 cancer cell lines.
The inhibitory effect of Decitabine was evaluated on the NALM-6 cell proliferation, followed by manual cell counting after 24, 48, and 72 hours. The cell viability of the treated groups with 1 μM of Decitabine partially decreased cell viability in comparison to untreated (control) groups. Exposure to Decitabine with a concentration of 1 μM decreased cell viability from 99% to 90% after 24 hrs, to 89% after 48 hrs, and from 99% to 89% after 72 hrs (Fig. 1).
The HDAC3 gene expression in the NALM-6 and control groups were analyzed before and after Decitabine treatment. The results show that the expression of the HDAC3 gene was significantly reduced in NALM-6 cell lines after Decitabine treatment (1 μM). (Fig. 2A). Moreover, HDAC7 gene expression in NALM-6 and normal human blood cells was measured before/after Decitabine treatment. The HDAC7 gene expression was significantly reduced in NALM-6 cancer cell lines after treatment with Decitabine (1 μM) (Fig. 2B).
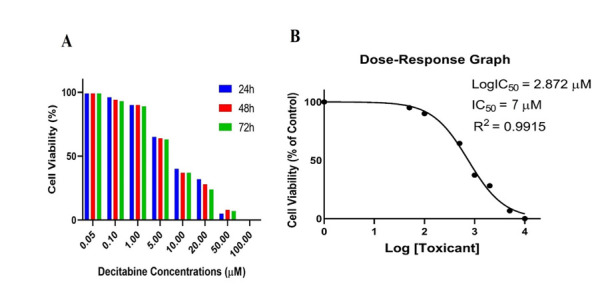 Fig. 1 Cell viability and IC50. (Dalvand S, et al., 2021)
Fig. 1 Cell viability and IC50. (Dalvand S, et al., 2021)
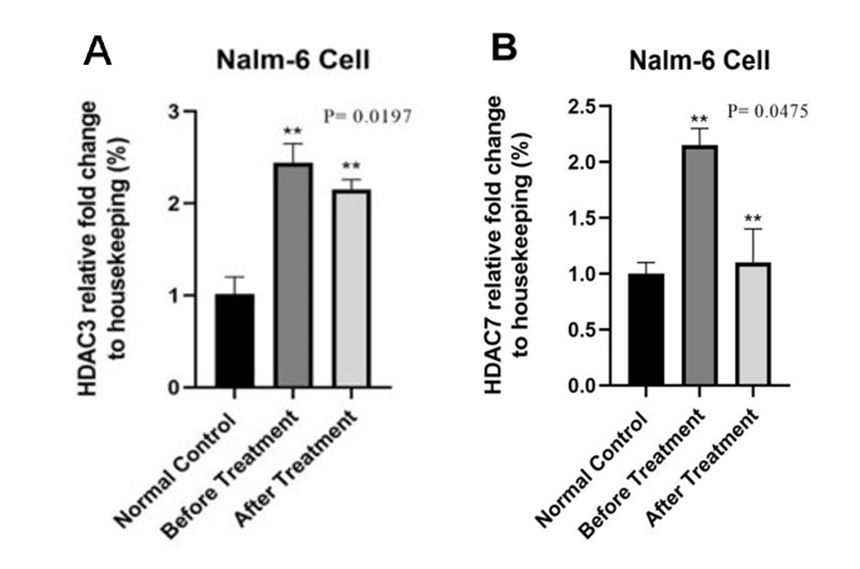 Fig. 2 (A) HDAC3 expression in NALM-6 and normal control groups; (B) The chart of HDAC7 gene expression in NALM-6 and normal control groups. (Dalvand S, et al., 2021)
Fig. 2 (A) HDAC3 expression in NALM-6 and normal control groups; (B) The chart of HDAC7 gene expression in NALM-6 and normal control groups. (Dalvand S, et al., 2021)
Overexpressing AIOLOS Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Suppresses Apoptosis in Nalm-6 Cells
The AIOLOS gene is important in the control of mature B-lymphocyte differentiation and proliferation. In the present study, Nalm-6 cells were divided into three groups: the untransfected control (UT), the lentiviral vector control (Lenti-Mock), and the AIOLOS-overexpressing (Lenti-AIOLOS) group. Lenti-AIOLOS Nalm-6 cells were constructed by lentiviral transduction, followed by cell proliferation assay, cell-cycle analysis, and apoptosis assay, to evaluate the effects of AIOLOS on proliferation, cell cycle distribution, and apoptosis of Nalm-6 cells in vitro.
Nalm-6 cells were infected with lentivirus vector pWPT-PURO-GFP-AIOLOS. As a control, Nalm-6 cells were either infected with a lentivirus vector expressing GFP or not. At precisely 96 h after infection of Nalm-6 cells, the infection efficiency was detected using a fluorescence microscope. A large number of cells emitted bright green fluorescence, which represented high infection efficiency (Fig. 3A-F). AIOLOS mRNA and protein expression levels in Nalm-6 cells of the three groups were determined by qRT-PCR and western blot assays on day 7 after infection. qRT-PCR demonstrated that the expression level of AIOLOS mRNA in Nalm-6 cells of the Lenti-AIOLOS group markedly increased compared with that of the Lenti-Mock group and UT group, which was consistent with the increase in AIOLOS protein expression (Fig. 3G and H).
As shown in Fig. 4, the proliferation of Nalm-6 cells in the Lenti-AIOLOS group was reduced by 16% on day 8 compared with that in the UT group cells (P>0.05). The reduction peaked at 29% on day 10 (P<0.05). The results indicated that overexpression of AIOLOS suppressed the growth of Nalm-6 cells to some degree. The cell cycle of Nalm-6 cells in the Lenti-AIOLOS, Lenti-Mock, and UT groups was characterized by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis on day 9 after transfection. As shown in Fig. 5, the percentage of Nalm-6 cells in the G0/G1 phase increased from 70.4 (UT) to 84.1% (Lenti-AIOLOS) (P<0.01), and the S-phase cells decreased from 20.3 (UT) to 11.7% (Lenti-AIOLOS) (P<0.01). The data indicated that upregulation of AIOLOS expression arrested Nalm-6 cells at the G0/G1 phase, which possibly contributed to the growth inhibition of Nalm-6 cells. As shown in Fig. 6, total apoptotic cells were significantly decreased in AIOLOS-transfected Nalm-6 cells (10.75%) compared with those in the Lenti-Mock (17.00%) or UT groups (19.05%) (P<0.01). These data suggest that overexpression of AIOLOS suppresses cell apoptosis in Nalm-6 cells.
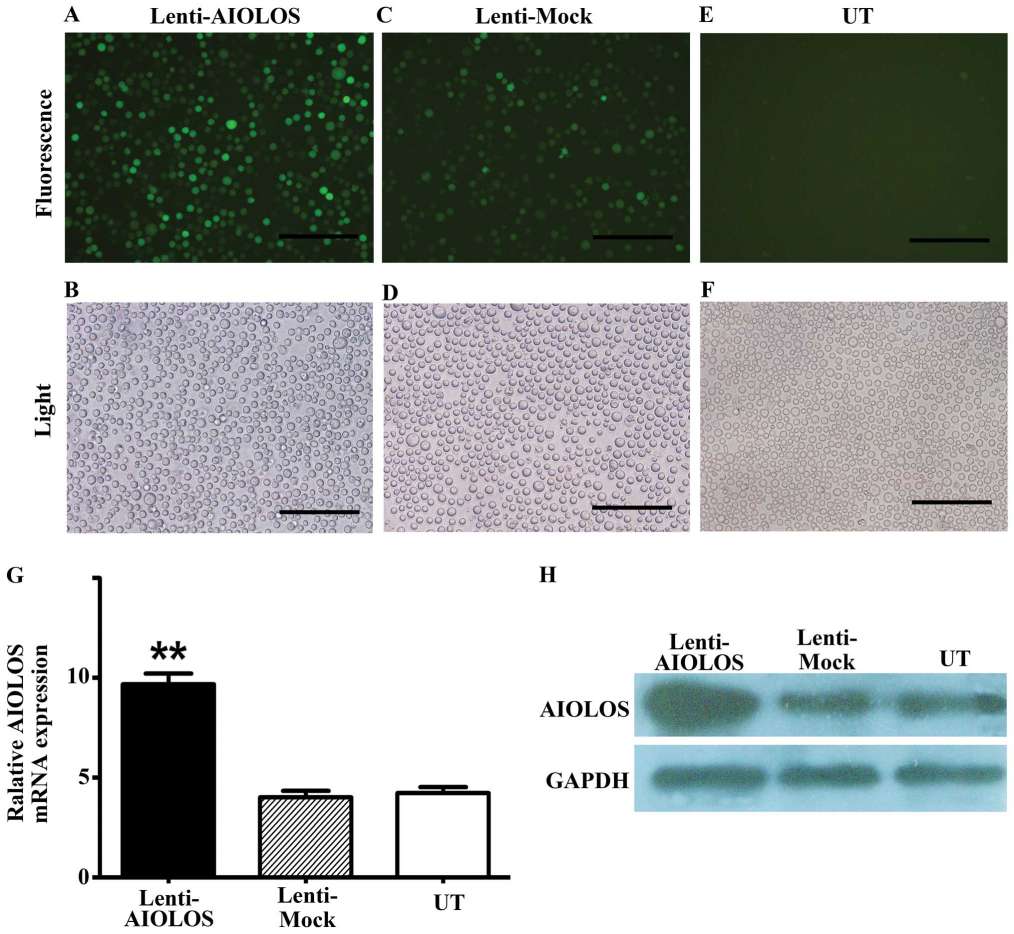 Fig. 3 Determination of lentiviral transduction efficiency and expression level of AIOLOS in Nalm-6 cells of the Lenti-AIOLOS group. (Zhuang Y, et al., 2014)
Fig. 3 Determination of lentiviral transduction efficiency and expression level of AIOLOS in Nalm-6 cells of the Lenti-AIOLOS group. (Zhuang Y, et al., 2014)
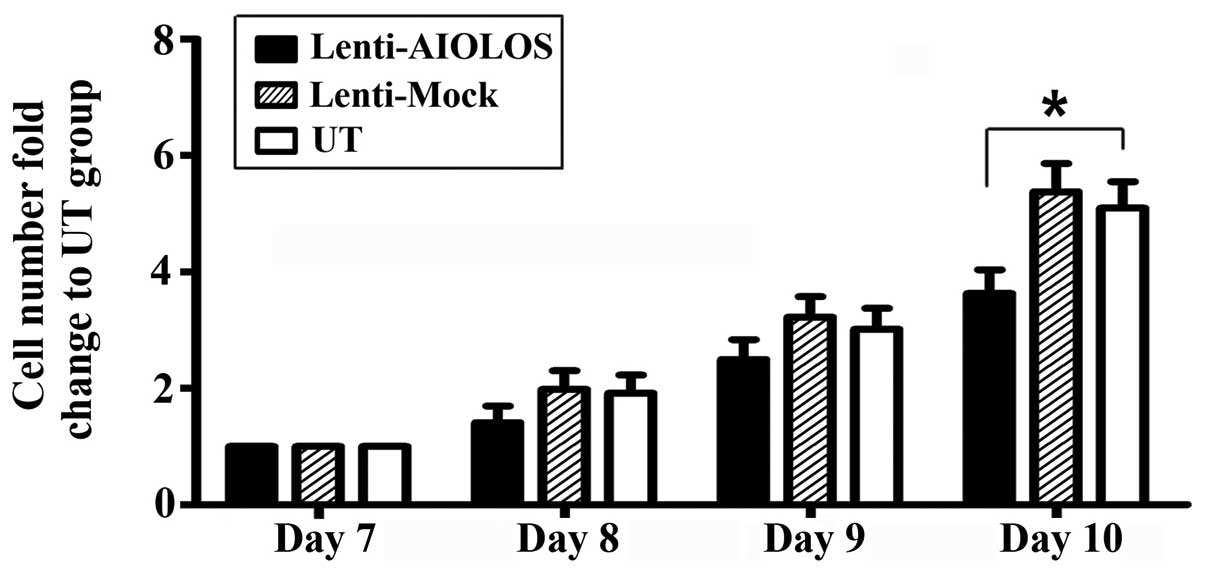 Fig. 4 Effect of AIOLOS on the proliferation of Nalm-6 cells. (Zhuang Y, et al., 2014)
Fig. 4 Effect of AIOLOS on the proliferation of Nalm-6 cells. (Zhuang Y, et al., 2014)
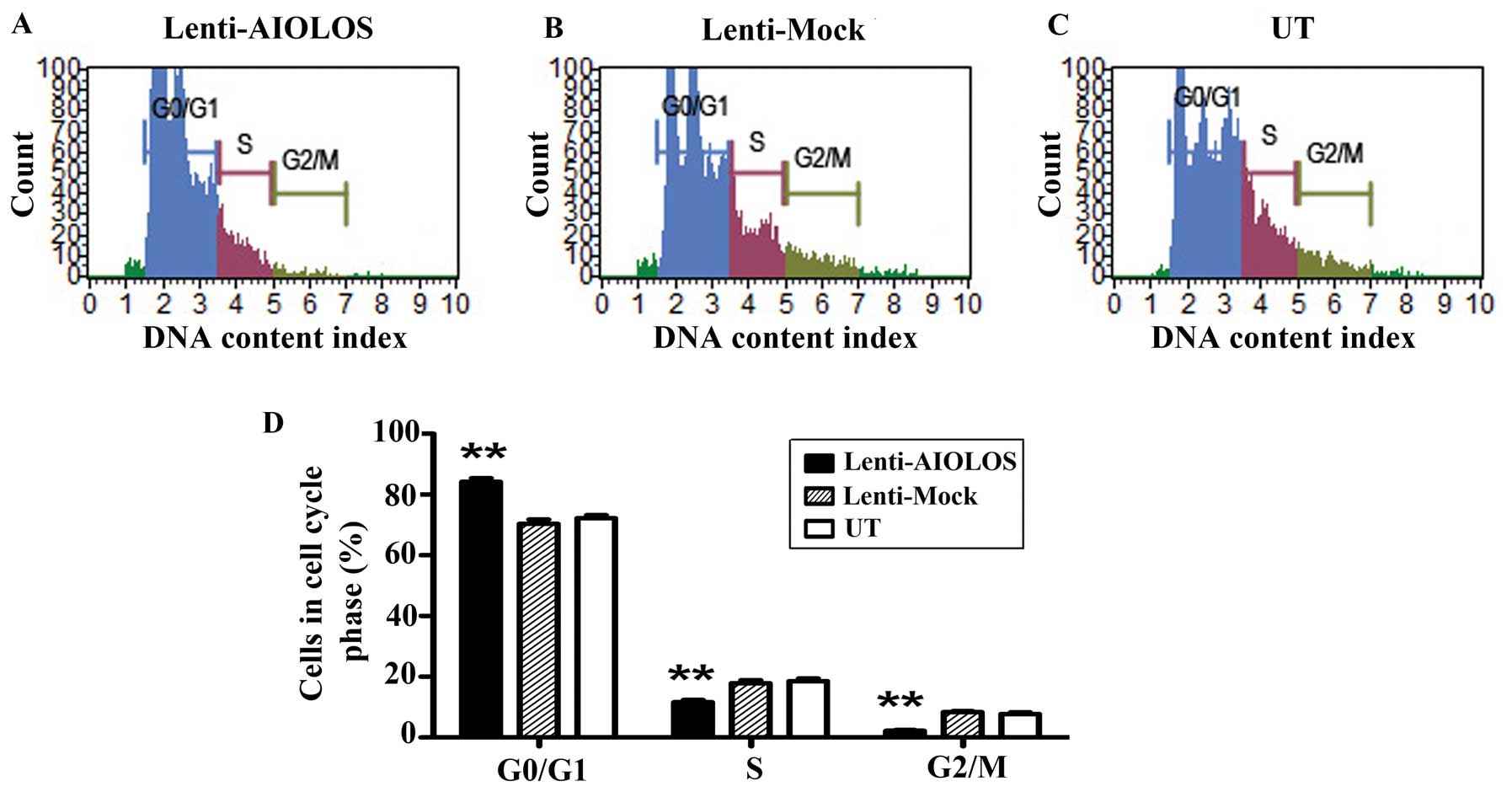 Fig. 5 Effect of AIOLOS on cell cycle distribution in Nalm-6 cells. (Zhuang Y, et al., 2014)
Fig. 5 Effect of AIOLOS on cell cycle distribution in Nalm-6 cells. (Zhuang Y, et al., 2014)
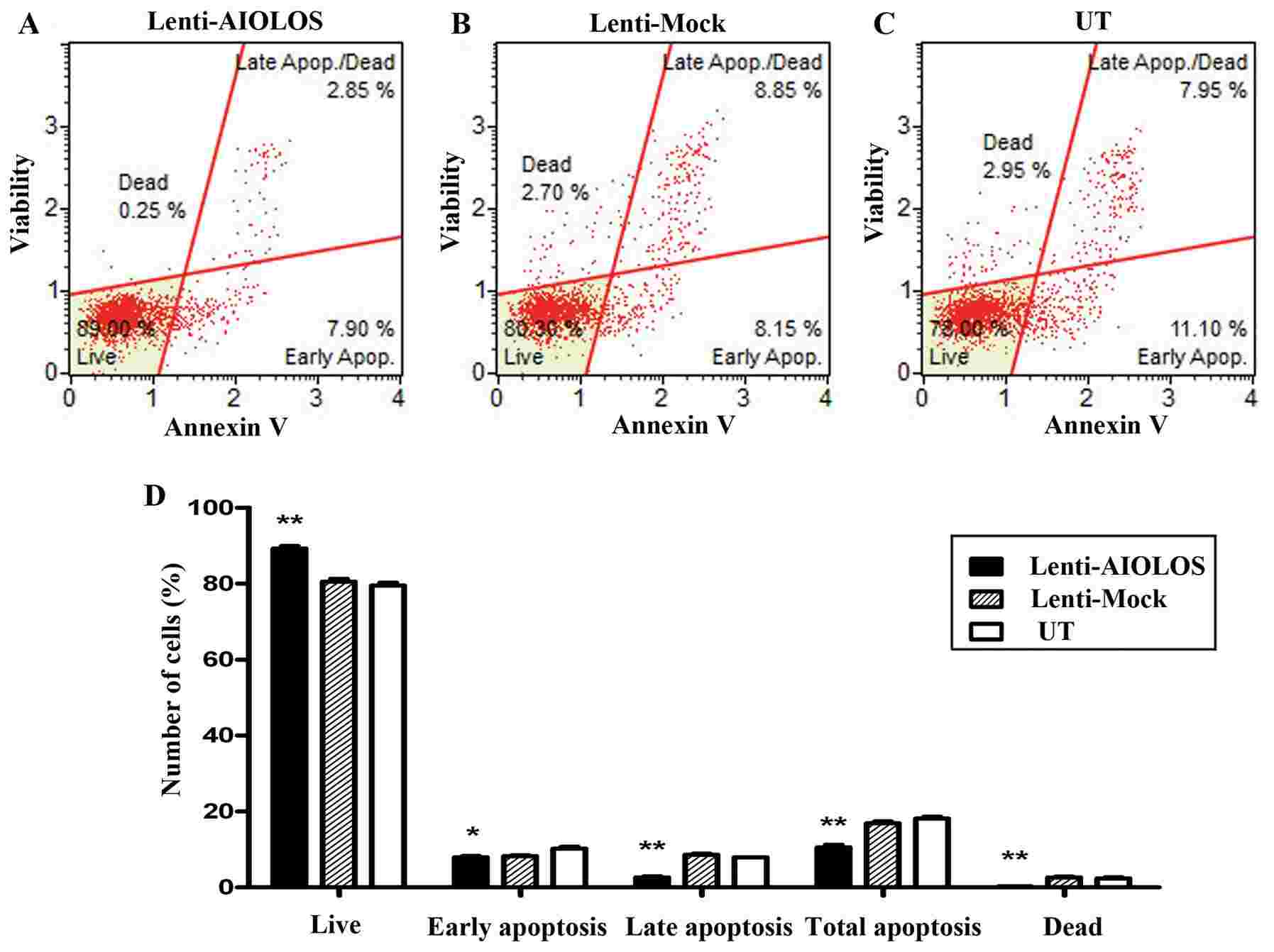 Fig. 6 Effect of AIOLOS on Nalm-6 cell apoptosis. (Zhuang Y, et al., 2014)
Fig. 6 Effect of AIOLOS on Nalm-6 cell apoptosis. (Zhuang Y, et al., 2014)
The transfection efficiency mainly depends on what transfection reagents are used. Here’s an article for your reference: Mascarenhas L, Stripecke R, Case S S, et al. Gene delivery to human B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells[J]. Blood, 1998, 92(10): 3537-3545.
NALM-6 cells exhibit properties representative of B-cell precursor ALL and are commonly used in research to understand the biology and therapeutic responses of this leukemia subtype.
NALM-6 cells were established from the peripheral blood of a 19-year-old man with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in relapse in 1976, providing a relevant model for studying this aggressive form of leukemia.
NALM-6 cells are extensively utilized in preclinical studies, drug screening assays, and in vitro experiments to evaluate the efficacy of potential anti-leukemic agents and elucidate the underlying mechanisms of leukemia pathogenesis.
Average Rating: 5.0 | 3 Scientist has reviewed this product
Satisfied
I am extremely satisfied with Creative Bioarray's products and services and will continue to choose them for my research needs.
09 Feb 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Valuable guidance
The support team of Creative Bioarray was highly responsive and provided valuable guidance throughout the purchase process.
21 May 2023
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Reliability and efficiency
Creative Bioarray remains my go-to supplier for research materials due to their reliability and efficiency.
19 Feb 2024
Ease of use
After sales services
Value for money
Customer Support & Price Inquiry

